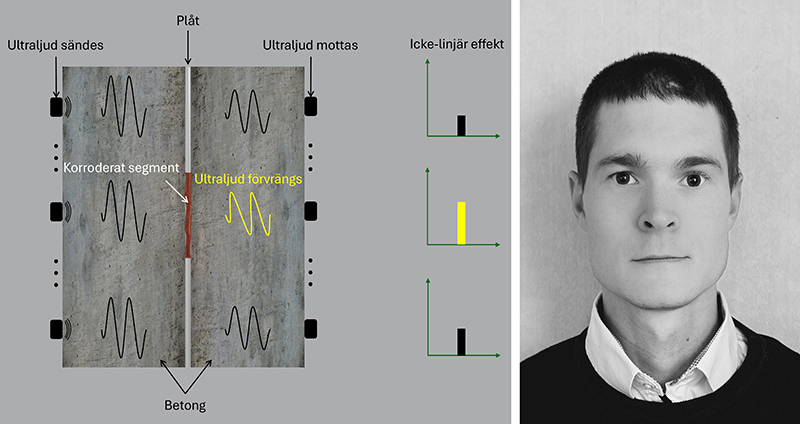
Generally, corrosion of steel in concrete is induced by either carbonation or by chlorides. Carbonation means that carbon dioxide in air reacts with calcium within the concrete. In the present study, samples made of steel cast in chloride containing mortar were exposed to different moisture conditions. The moisture condition was either static at a certain relative humidity or dynamic where the relative humidity was cycling between 75% and 100%
The work presented in this licentiate thesis has been carried out partly at the Division of Building Materials, Lund University, and partly at Swerea KIMAB, Stockholm.